- Home
- Science
- Science News
- New Low Cost Bacteria Powered Origami Battery Developed
New Low-Cost Bacteria-Powered Origami Battery Developed
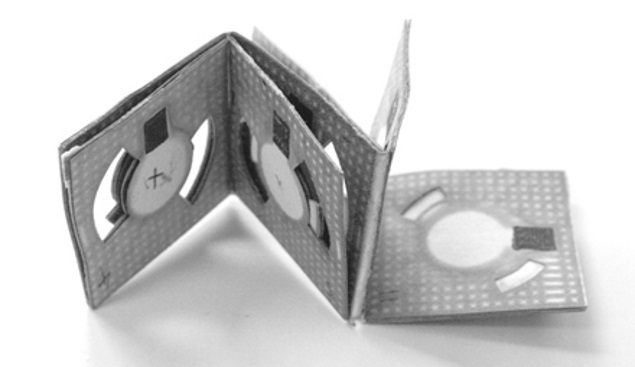
Seokheun Choi from the State University of New York at Binghamton developed the battery which generates power from microbial respiration and costs just $0.05 (roughly Rs. 3.2) to build.
It delivers enough energy to run a paper-based biosensor with nothing more than a drop of bacteria-containing liquid.
"Dirty water has a lot of organic matter. Any type of organic material can be the source of bacteria for the bacterial metabolism," Choi said.
The new method should be especially useful to anyone working in remote areas with limited resources, Choi said.
Since paper is inexpensive and readily available, many experts working on disease control and prevention have seized upon it as a key material in creating diagnostic tools for the developing world.
However, paper-based biosensors must be paired with hand-held devices for analysis.
Choi said he envisions a self-powered system in which a paper-based battery would create enough energy to run the biosensor.
Creating such a system is the goal of a three-year grant of nearly $300,000 (roughly Rs. 1.8 crores) he has received from the National Science Foundation in the US.
The battery, which folds into a square the size of a matchbook, uses an inexpensive air-breathing cathode created with nickel sprayed onto one side of ordinary office paper.
The anode is screen printed with carbon paints, creating a hydrophilic zone with wax boundaries.
The research is published in the journal Nano Energy.
Get your daily dose of tech news, reviews, and insights, in under 80 characters on Gadgets 360 Turbo. Connect with fellow tech lovers on our Forum. Follow us on X, Facebook, WhatsApp, Threads and Google News for instant updates. Catch all the action on our YouTube channel.
Related Stories
- Samsung Galaxy Unpacked 2026
- iPhone 17 Pro Max
- ChatGPT
- iOS 26
- Laptop Under 50000
- Smartwatch Under 10000
- Apple Vision Pro
- Oneplus 12
- OnePlus Nord CE 3 Lite 5G
- iPhone 13
- Xiaomi 14 Pro
- Oppo Find N3
- Tecno Spark Go (2023)
- Realme V30
- Best Phones Under 25000
- Samsung Galaxy S24 Series
- Cryptocurrency
- iQoo 12
- Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra
- Giottus
- Samsung Galaxy Z Flip 5
- Apple 'Scary Fast'
- Housefull 5
- GoPro Hero 12 Black Review
- Invincible Season 2
- JioGlass
- HD Ready TV
- Latest Mobile Phones
- Compare Phones
- Realme C83 5G
- Nothing Phone 4a Pro
- Infinix Note 60 Ultra
- Nothing Phone 4a
- Honor 600 Lite
- Nubia Neo 5 GT
- Realme Narzo Power 5G
- Vivo X300 FE
- MacBook Neo
- MacBook Pro 16-Inch (M5 Max, 2026)
- Tecno Megapad 2
- Apple iPad Air 13-Inch (2026) Wi-Fi + Cellular
- Tecno Watch GT 1S
- Huawei Watch GT Runner 2
- Xiaomi QLED TV X Pro 75
- Haier H5E Series
- Asus ROG Ally
- Nintendo Switch Lite
- Haier 1.6 Ton 5 Star Inverter Split AC (HSU19G-MZAID5BN-INV)
- Haier 1.6 Ton 5 Star Inverter Split AC (HSU19G-MZAIM5BN-INV)
















