- Home
- Science
- Science News
- Nasa's Ibex Defines Interstellar Magnetic Field
Nasa's Ibex Defines Interstellar Magnetic Field
Immediately after its 2008 launch, IBEX spotted a curiosity in a thin slice of space - more particles streamed in through a long, skinny swath in the sky than anywhere else.
The origin of the so-called IBEX ribbon was unknown - but its very existence opened doors to observing what lies outside the solar system.
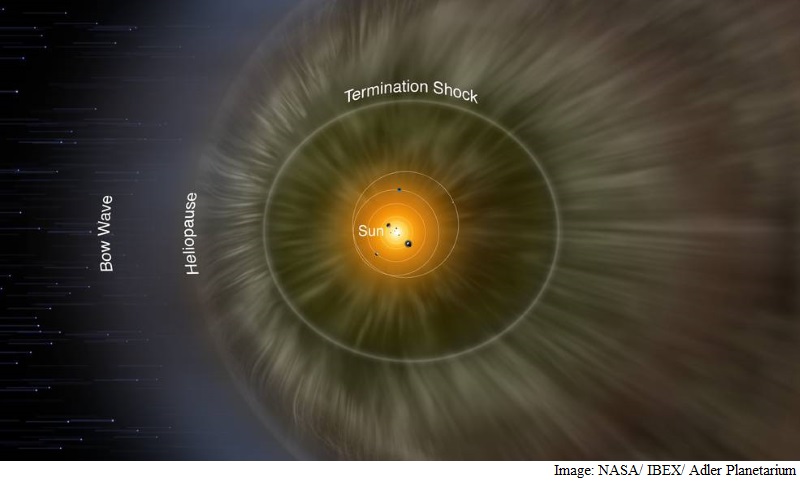
Now, a new study uses IBEX data and simulations of the interstellar boundary - which lies at the very edge of the giant magnetic bubble surrounding our solar system called the heliosphere - to better describe space in our galactic neighbourhood.
The study is based on one particular theory of the origin of the IBEX ribbon, in which the particles streaming in from the ribbon are actually solar material reflected back at us after a long journey to the edges of the sun's magnetic boundaries, researchers said.
A giant bubble, known as the heliosphere, exists around the sun and is filled with what is called solar wind, the sun's constant outflow of ionised gas, known as plasma. When these particles reach the edges of the heliosphere, their motion becomes more complicated, they said.
"The theory says that some solar wind protons are sent flying back towards the sun as neutral atoms after a complex series of charge exchanges, creating the IBEX ribbon," said Eric Zirnstein from Southwest Research Institute in US.
"Simulations and IBEX observations pinpoint this process - which takes anywhere from three to six years on average - as the most likely origin of the IBEX ribbon," said Zirnstein.
The directions of different ribbon particles shooting back toward Earth are determined by the characteristics of the interstellar magnetic field.
For instance, simulations show that the most energetic particles come from a different region of space than the least energetic particles, which gives clues as to how the interstellar magnetic field interacts with the heliosphere, researchers said.
For the study, such observations were used to seed simulations of the ribbon's origin. Not only do these simulations correctly predict the locations of neutral ribbon particles at different energies, but the deduced interstellar magnetic field agrees with Voyager 1 measurements, the deflection of interstellar neutral gases, and observations of distant polarised starlight.
"Voyager 1 crossed the termination shock at 94 astronomical units (AU) from the sun, and Voyager 2 at 84 AU," said Zirnstein. One AU is equal to about 150 million kilometres, the average distance between Earth and the sun.
"That difference of almost 150 million kilometres was mostly explained by a strong, very tilted interstellar magnetic field pushing on the heliosphere," said Zirnstein. The study was published in Astrophysical Journal.
Get your daily dose of tech news, reviews, and insights, in under 80 characters on Gadgets 360 Turbo. Connect with fellow tech lovers on our Forum. Follow us on X, Facebook, WhatsApp, Threads and Google News for instant updates. Catch all the action on our YouTube channel.
Related Stories
- Samsung Galaxy Unpacked 2025
- ChatGPT
- Redmi Note 14 Pro+
- iPhone 16
- Apple Vision Pro
- Oneplus 12
- OnePlus Nord CE 3 Lite 5G
- iPhone 13
- Xiaomi 14 Pro
- Oppo Find N3
- Tecno Spark Go (2023)
- Realme V30
- Best Phones Under 25000
- Samsung Galaxy S24 Series
- Cryptocurrency
- iQoo 12
- Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra
- Giottus
- Samsung Galaxy Z Flip 5
- Apple 'Scary Fast'
- Housefull 5
- GoPro Hero 12 Black Review
- Invincible Season 2
- JioGlass
- HD Ready TV
- Laptop Under 50000
- Smartwatch Under 10000
- Latest Mobile Phones
- Compare Phones
- OPPO A6v 5G
- OPPO A6i+ 5G
- Realme 16 5G
- Redmi Turbo 5
- Redmi Turbo 5 Max
- Moto G77
- Moto G67
- Realme P4 Power 5G
- HP HyperX Omen 15
- Acer Chromebook 311 (2026)
- Lenovo Idea Tab Plus
- Realme Pad 3
- HMD Watch P1
- HMD Watch X1
- Haier H5E Series
- Acerpure Nitro Z Series 100-inch QLED TV
- Asus ROG Ally
- Nintendo Switch Lite
- Haier 1.6 Ton 5 Star Inverter Split AC (HSU19G-MZAID5BN-INV)
- Haier 1.6 Ton 5 Star Inverter Split AC (HSU19G-MZAIM5BN-INV)

















