- Home
- Science
- Science News
- Nasa 'Hedgehog' Robots to Hop and Tumble in Microgravity
Nasa 'Hedgehog' Robots to Hop and Tumble in Microgravity
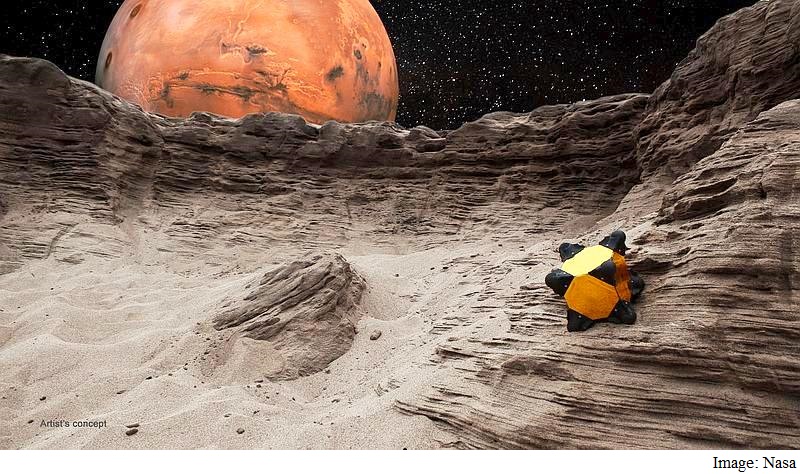

Traditional Mars rovers roll around on wheels and they cannot operate upside-down in rough terrain. To overcome this problem, Nasa scientists are building a Hedgehog robot that will hop and tumble on the surface instead of rolling on wheels.
Along with researchers from Stanford University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, the Nasa team is building a five-kg robot that is specifically designed to overcome the challenges of traversing small bodies like an asteroid or a comet with low-gravity conditions and rough surfaces.
"Hedgehog is shaped like a cube and can operate no matter which side it lands on," said Issa Nesnas, leader of the team from Nasa's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, in a statement.
The construction of a Hedgehog robot is relatively low-cost compared to a traditional rover and several could be packaged together for flight.
The mothership could release many robots at once or in stages, letting them spread out to make discoveries on a world never traversed before.
The basic concept is a cube with spikes that moves by spinning and braking internal flywheels. The JPL Hedgehog prototype has eight spikes and three flywheels.
The spikes protect the robot's body from the terrain and act as feet while hopping and tumbling.
"The spikes could also house instruments such as thermal probes to take the temperature of the surface as the robot tumbles," Nesnas added.
Two Hedgehog prototypes -- one from Stanford and one from JPL - were tested aboard Nasa's C-9 aircraft for microgravity research in June 2015.
During 180 parabolas, over the course of four flights, these robots demonstrated several types of manoeuvres that would be useful for getting around on small bodies with reduced gravity.
Researchers tested these manoeuvres on different materials that mimic a wide range of surfaces: sandy, rough and rocky, slippery and icy, and soft and crumbly.
"We demonstrated for the first time our Hedgehog prototypes performing controlled hopping and tumbling in comet-like environments," noted Robert Reid, lead engineer on the project at JPL.
The team hope the robot could weigh more than nine kg with instruments such as cameras and spectrometers.
The researchers are currently working on Hedgehog's autonomy, trying to increase how much the robots can do by themselves without instructions from Earth.
Their idea is that an orbiting mothership would relay signals to and from the robot, similar to how Nasa's Mars rovers Curiosity and Opportunity communicate via satellites orbiting Mars.
The mothership would also help the robots navigate and determine their positions, the space agency noted.
Get your daily dose of tech news, reviews, and insights, in under 80 characters on Gadgets 360 Turbo. Connect with fellow tech lovers on our Forum. Follow us on X, Facebook, WhatsApp, Threads and Google News for instant updates. Catch all the action on our YouTube channel.
Related Stories
- Samsung Galaxy Unpacked 2026
- iPhone 17 Pro Max
- ChatGPT
- iOS 26
- Laptop Under 50000
- Smartwatch Under 10000
- Apple Vision Pro
- Oneplus 12
- OnePlus Nord CE 3 Lite 5G
- iPhone 13
- Xiaomi 14 Pro
- Oppo Find N3
- Tecno Spark Go (2023)
- Realme V30
- Best Phones Under 25000
- Samsung Galaxy S24 Series
- Cryptocurrency
- iQoo 12
- Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra
- Giottus
- Samsung Galaxy Z Flip 5
- Apple 'Scary Fast'
- Housefull 5
- GoPro Hero 12 Black Review
- Invincible Season 2
- JioGlass
- HD Ready TV
- Latest Mobile Phones
- Compare Phones
- Lava Bold 2 5G
- Motorola Edge 70 Fusion+
- iQOO Z11x 5G
- Vivo Y51 Pro 5G
- Itel Zeno 100
- Poco C85x 5G
- Realme Note 80
- Vivo V70 FE
- MacBook Neo
- MacBook Pro 16-Inch (M5 Max, 2026)
- Tecno Megapad 2
- Apple iPad Air 13-Inch (2026) Wi-Fi + Cellular
- Tecno Watch GT 1S
- Huawei Watch GT Runner 2
- Xiaomi QLED TV X Pro 75
- Haier H5E Series
- Asus ROG Ally
- Nintendo Switch Lite
- Haier 1.6 Ton 5 Star Inverter Split AC (HSU19G-MZAID5BN-INV)
- Haier 1.6 Ton 5 Star Inverter Split AC (HSU19G-MZAIM5BN-INV)