- Home
- Science
- Science News
- Modified iPhone Helps Regulate Blood Sugar in Diabetes Patients: Study
Modified iPhone Helps Regulate Blood Sugar in Diabetes Patients: Study
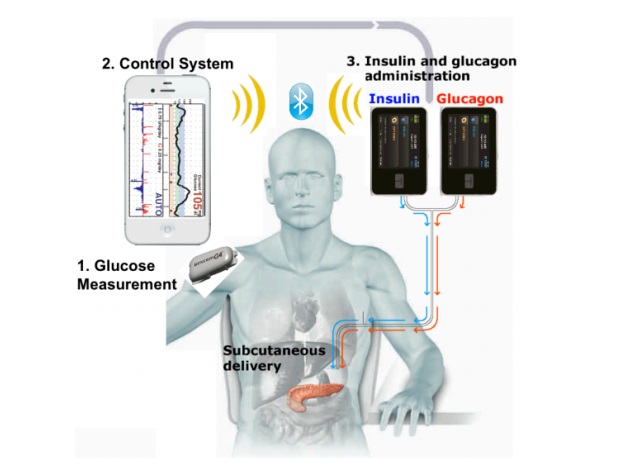
The so-called "bionic pancreas" is the latest in the search to improve the lives of people who have type 1 diabetes, which means their bodies do not produce insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar.
Three million people in the United States have type 1 diabetes, which is far less common than type 2 diabetes. It is commonly known as juvenile diabetes because it tends to appear in children and young adults.
People with type 1 diabetes must prick themselves for blood samples multiple times daily in order to monitor their glucose levels, and then either inject insulin or receive it from a pump.
The new method involved an iPhone 4S, which ran a control algorithm for insulin and glucagon, combined with a tiny needle that is inserted under the skin to monitor real-time glucose levels.
A total of 52 adults and youths tried the combination for five days.
The patients using the bionic pancreas had fewer interventions for low blood sugar and showed "significant improvements" in overnight blood glucose levels over what they experienced normally, said the researchers.
"The bionic pancreas system reduced the average blood glucose to levels that have been shown to dramatically reduce the risk of diabetic complications," said researcher Steven Russell, assistant professor of medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital.
"This is tremendously difficult with currently available technology."
More research is needed before the device can be made available for sale, the authors said.
The findings were published Sunday in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Get your daily dose of tech news, reviews, and insights, in under 80 characters on Gadgets 360 Turbo. Connect with fellow tech lovers on our Forum. Follow us on X, Facebook, WhatsApp, Threads and Google News for instant updates. Catch all the action on our YouTube channel.
- Samsung Galaxy Unpacked 2026
- iPhone 17 Pro Max
- ChatGPT
- iOS 26
- Laptop Under 50000
- Smartwatch Under 10000
- Apple Vision Pro
- Oneplus 12
- OnePlus Nord CE 3 Lite 5G
- iPhone 13
- Xiaomi 14 Pro
- Oppo Find N3
- Tecno Spark Go (2023)
- Realme V30
- Best Phones Under 25000
- Samsung Galaxy S24 Series
- Cryptocurrency
- iQoo 12
- Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra
- Giottus
- Samsung Galaxy Z Flip 5
- Apple 'Scary Fast'
- Housefull 5
- GoPro Hero 12 Black Review
- Invincible Season 2
- JioGlass
- HD Ready TV
- Latest Mobile Phones
- Compare Phones
- Realme C83 5G
- Nothing Phone 4a Pro
- Infinix Note 60 Ultra
- Nothing Phone 4a
- Honor 600 Lite
- Nubia Neo 5 GT
- Realme Narzo Power 5G
- Vivo X300 FE
- MacBook Neo
- MacBook Pro 16-Inch (M5 Max, 2026)
- Tecno Megapad 2
- Apple iPad Air 13-Inch (2026) Wi-Fi + Cellular
- Tecno Watch GT 1S
- Huawei Watch GT Runner 2
- Xiaomi QLED TV X Pro 75
- Haier H5E Series
- Asus ROG Ally
- Nintendo Switch Lite
- Haier 1.6 Ton 5 Star Inverter Split AC (HSU19G-MZAID5BN-INV)
- Haier 1.6 Ton 5 Star Inverter Split AC (HSU19G-MZAIM5BN-INV)












