- Home
- Laptops
- Laptops News
- Apple patches serious 'triple handshake' bug with iOS 7.1.1, OS X updates
Apple patches serious 'triple handshake' bug with iOS 7.1.1, OS X updates
By NDTV Correspondent | Updated: 23 April 2014 21:02 IST
Advertisement
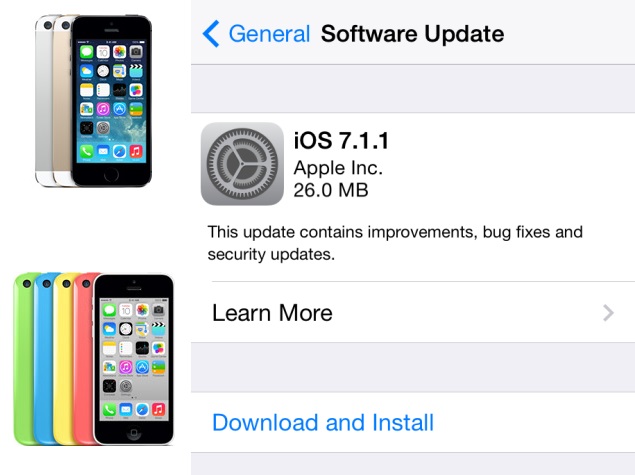
Yet another major security flaw has come to light, and Apple has released updates for its two major operating systems to address it. The HTTP "triple handshake" bug is considered extremely serious because it can be exploited to allow attackers to circumvent encryption on communications which rely on SSL for security.
Ars Technica reports that devices running iOS 7, OS X 10.9.x (Mavericks) and OS X 10.8.x (Mountain Lion) are vulnerable unless they install the latest updates. Apple's release notes for iOS 7.1.1 describe four security-related fixes, including one for the triple handshake bug, known as CVE-1295..
Apple's description doesn't include a severity rating, but describes the potential impact as "An attacker with a privileged network position may capture data or change the operations performed in sessions protected by SSL."
The bug allows attackers trick a client into sending them credentials by spoofing a connection to another trusted server. The credentials could then be reused with other servers, which would simply accept them without question. Apple's fix now ensures that credentials are verified against the original SSL certificate for each connection.
The update comes hot on the heels of another disclosure by Apple that its AirPort Extreme and AirPort Time Capsule routers were vulnerable to the Heartbleed OpenSSL bug. A patch for those products has also been released.
Apple was also forced to issue emergency OS updates in February this year for a security bug dubbed GoToFail, which tricked Web browsers into accepting SSL certificates without legitimate signatures.
Ars Technica reports that devices running iOS 7, OS X 10.9.x (Mavericks) and OS X 10.8.x (Mountain Lion) are vulnerable unless they install the latest updates. Apple's release notes for iOS 7.1.1 describe four security-related fixes, including one for the triple handshake bug, known as CVE-1295..
Apple's description doesn't include a severity rating, but describes the potential impact as "An attacker with a privileged network position may capture data or change the operations performed in sessions protected by SSL."
The bug allows attackers trick a client into sending them credentials by spoofing a connection to another trusted server. The credentials could then be reused with other servers, which would simply accept them without question. Apple's fix now ensures that credentials are verified against the original SSL certificate for each connection.
The update comes hot on the heels of another disclosure by Apple that its AirPort Extreme and AirPort Time Capsule routers were vulnerable to the Heartbleed OpenSSL bug. A patch for those products has also been released.
Apple was also forced to issue emergency OS updates in February this year for a security bug dubbed GoToFail, which tricked Web browsers into accepting SSL certificates without legitimate signatures.
Comments
For the latest tech news and reviews, follow Gadgets 360 on X, Facebook, WhatsApp, Threads and Google News. For the latest videos on gadgets and tech, subscribe to our YouTube channel. If you want to know everything about top influencers, follow our in-house Who'sThat360 on Instagram and YouTube.
Related Stories
Popular on Gadgets
- Samsung Galaxy Unpacked 2025
- ChatGPT
- Redmi Note 14 Pro+
- iPhone 16
- Apple Vision Pro
- Oneplus 12
- OnePlus Nord CE 3 Lite 5G
- iPhone 13
- Xiaomi 14 Pro
- Oppo Find N3
- Tecno Spark Go (2023)
- Realme V30
- Best Phones Under 25000
- Samsung Galaxy S24 Series
- Cryptocurrency
- iQoo 12
- Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra
- Giottus
- Samsung Galaxy Z Flip 5
- Apple 'Scary Fast'
- Housefull 5
- GoPro Hero 12 Black Review
- Invincible Season 2
- JioGlass
- HD Ready TV
- Laptop Under 50000
- Smartwatch Under 10000
- Latest Mobile Phones
- Compare Phones
Latest Gadgets
- Vivo Y19 5G
- iQOO Z10 Turbo Pro
- iQOO Z10 Turbo
- CMF by Nothing Phone 2 Pro
- Motorola Edge 60
- Motorola Edge 60 Pro
- Motorola Razr 60
- Motorola Razr 60 Ultra
- Asus ROG Zephyrus G16 (2025)
- Asus ROG Zephyrus G14 (2025)
- Honor Pad GT
- Vivo Pad SE
- Moto Watch Fit
- Honor Band 10
- Xiaomi X Pro QLED 2025 (43-Inch)
- Xiaomi X Pro QLED 2025 (55-Inch)
- Asus ROG Ally
- Nintendo Switch Lite
- Toshiba 1.8 Ton 5 Star Inverter Split AC (RAS-24TKCV5G-INZ / RAS-24TACV5G-INZ)
- Toshiba 1.5 Ton 5 Star Inverter Split AC (RAS-18PKCV2G-IN / RAS-18PACV2G-IN)
© Copyright Red Pixels Ventures Limited 2025. All rights reserved.

















